how thick should driveway concrete be

As a concrete driveway expert, I often get asked, "How thick should a concrete driveway be?"
The ideal concrete driveway thickness depends on various factors such as soil conditions, climate, expected traffic loads, and local building codes. For residential concrete driveways, a 4-inch thickness is typically sufficient, while commercial driveways often require a minimum thickness of 6 inches thick.
In this blog post, we'll dive into the topic of concrete driveway thickness, explore the differences between residential and commercial concrete driveways, and discuss the minimum concrete driveway thickness for different scenarios. So, let's get started!
MInimum concrete thickness for driveway's
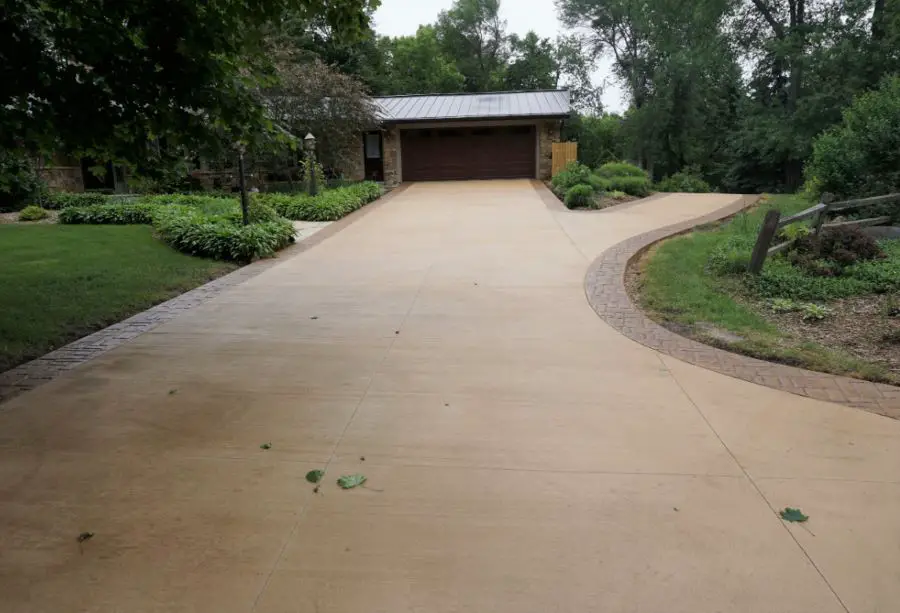

When deciding on the thickness of your new concrete driveway, it's essential to consider the weight and type of vehicles regularly using the driveway.
Let's take a look at different vehicles and their weights to help guide you in determining the appropriate concrete driveway thickness for your needs.
Concrete thickness for passenger vehicles and light trucks
Most standard passenger vehicles, such as sedans, SUVs, and minivans, weigh between 3,000 and 4,500 pounds. Light trucks, including pickups and small delivery vans, can weigh between 4,500 and 6,000 pounds. For most residential concrete driveways that will primarily be used by these types of vehicles, a 4-inch thick concrete slab is usually sufficient to support the weight and provide durability.
Concrete thickness for RVs, Campers, and Boat Trailers
Recreational vehicles (RVs), campers, and boat trailers can vary significantly in weight, depending on their size and type. Smaller campers and boat trailers may weigh between 3,000 and 5,000 pounds, while larger RVs and trailers can weigh up to 15,000 pounds or more.
If your driveway will be used to park or maneuver these heavy vehicles, you may want to consider a 5- or 6-inch thick concrete slab to provide the necessary support and prevent damage over time.
Concrete thickness for Commercial or Construction Vehicles
Commercial vehicles and heavy trucks, such as delivery trucks, garbage trucks, or dump trucks, can weigh anywhere from 10,000 to 80,000 pounds or more. If your business requires a driveway to accommodate these types of vehicles, thicker concrete slabs of at least 6 - 8 inches are necessary.
In some cases, depending on the frequency and load distribution, a thicker slab with steel reinforcement may be required to ensure the proper structural support.
| Vehicle Type | Typical Weight Range (pounds) | Suggested Concrete Thickness (inches) |
|---|---|---|
| Passenger Vehicles | 3,000 - 4,500 | 4 |
| Light Trucks | 4,500 - 6,000 | 4 |
| RVs, Campers, Boat Trailers | 3,000 - 15,000 | 5 - 6 |
| Commercial Vehicles | 10,000 - 80,000 | 6+ (depending on load and frequency) |
Factors That Affect The Minimum Thickness of Concrete Driveways
Several factors come into play when determining the right concrete thickness for your driveway. These include:

Soil Conditions and Their Impact on Concrete Driveway Thickness
Your underlying soil conditions play a crucial role in determining the appropriate concrete driveway thickness. Different types of soils have varying load-bearing capacities, which directly affect the performance and longevity of your concrete driveway.
There are several types of soil, each with its characteristics that influence the stability and support capacity of a concrete driveway. Some common soil types include:
- Expansive soil like clay: Clay soils are cohesive and have a high load-bearing capacity, but they also tend to expand and contract with moisture content changes, which can lead to movement and cracking in a concrete slab.
- Organic soil like silt: Silt is a fine-grained soil with low permeability, making it prone to waterlogging and compaction. Its load-bearing capacity is generally lower than that of clay or sandy soils.
- Mixed Sand: Sandy soils have excellent drainage properties and a moderate load-bearing capacity, but they can be prone to erosion and instability if not properly compacted.
- Gravel: Gravelly soils offer good drainage and a high load-bearing capacity but may require additional compaction efforts to achieve a stable base for a concrete driveway.
Recommended Sub-Base For Residential Driveways
A well-graded, compacted gravel sub-base is critical for the long-term performance of a concrete driveway. The type of gravel used can impact the stability and drainage properties of the driveway.
It's generally recommended to use crushed stone material or crushed angular gravel with a mix of particle sizes for the sub-base. This type of gravel locks together better than rounded gravel, which helps increase a driveway's load-carrying capacity.
A common recommendation is to use a 4-inch layer of compacted 3/4-inch crushed stone or similar material for the sub-base in non-freeze-thaw environments. Another 2" - 12" of gravel in high freeze/thaw areas may be necessary depending on existing soil conditions.
This provides a stable platform for the concrete, helps distribute the load evenly, and allows for proper drainage, reducing the risk of water-related issues such as frost heave and soil expansion.
how Climate and Temperatures affect concrete
Climate can also impact the reason to increase the average thickness. In areas prone to freezing and thawing cycles, a thicker concrete driveway may be necessary to resist frost heave and cracking.
Additionally, regions with high temperatures may require thicker concrete to prevent buckling and other heat-related damage.
is rebar needed in a concrete driveway?
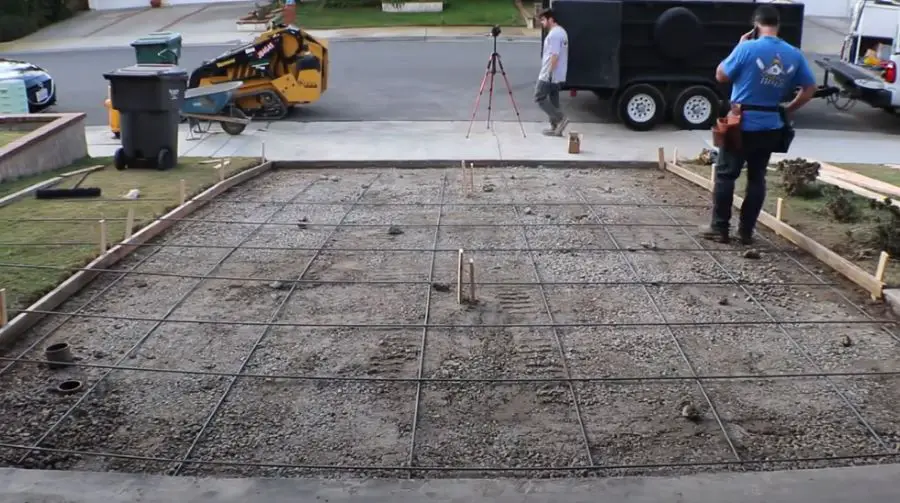
The Benefits of Rebar, Wire Mesh, and Fiber Mesh Reinforcement in Concrete Driveways:
Reinforcing concrete driveways with rebar, wire mesh, or fiber mesh can significantly improve their strength, support, and durability.
Each reinforcement method offers unique advantages that contribute to the overall performance of the concrete driveway. Let's explore the benefits of each type and how they add strength and support.
Using rebar reinforcement in your concrete driveway
Rebar, short for steel reinforcing bar, is made of steel and is commonly used to add additional structural support to concrete. Rebar provides several benefits for concrete driveways:
- Increased Tensile Strength: Concrete has excellent compressive strength but relatively low tensile strength. Rebar reinforcement helps to counteract the tensile forces in the concrete, preventing cracks from forming and spreading.
- Improved Load-Bearing Capacity: The added strength provided by rebar allows the concrete driveway to support heavier loads and resist damage from heavy vehicles or equipment.
- Enhanced Durability: Rebar helps maintain the structural integrity of the concrete slab, even in the face of external forces such as freeze-thaw cycles, soil movement, or heavy loads.
wire mesh reinforcement
Wire mesh, also known as welded wire fabric, is a grid of steel wires that is laid within the concrete slab before pouring. It provides several advantages for concrete driveways:
- Crack Control: Wire mesh helps to distribute stress evenly throughout the concrete slab, reducing the risk of cracks forming or propagating.
- Improved Flexibility: The grid pattern structure of wire mesh allows the concrete to flex and adapt to minor movements in the ground, preventing damage.
- Cost-Effective: Wire mesh is often less expensive than rebar, making it a more affordable reinforcement option for some projects.
Fiber Mesh Reinforcement
Fiber mesh reinforcement consists of synthetic fibers, such as polypropylene or nylon, that are mixed into the concrete before pouring. This method offers unique benefits for concrete driveways:
- Micro-Crack Control: Fiber mesh helps to reduce the formation of micro-cracks in the concrete, which can eventually develop into larger cracks.
- Increased Resistance to Shrinkage: The fibers help to counteract the shrinkage forces that occur as the concrete cures, reducing the risk of cracking.
- Improved Impact Resistance: Fiber mesh can improve the concrete's resistance to impact and abrasion, helping to protect the driveway from wear and tear.
Placing concrete at the proper thickness is essential for both residential and commercial concrete driveways

The load-bearing capacity of a concrete driveway is directly related to its thickness. A thicker slab provides better support for the weight of vehicles and reduces the risk of cracking or other damage.
The increase in load-bearing capacity when adding an inch of concrete can be significant. For example, consider a driveway that is upgraded from 4 to 5 inches in thickness:
(How much weight can a 5-inch concrete driveway hold?)
- A 4-inch thick slab can support around 8,000 to 10,000 psf of load, while a 5-inch thick slab can support approximately 12,000 to 15,000 psf. This represents an increase in load-bearing capacity of around 4,000 to 5,000 psf.
Now, consider a driveway that is upgraded from 5 to 6 inches in thickness:
(How much weight can a 6-inch concrete driveway hold?)
- A 5-inch thick slab can support approximately 12,000 to 15,000 psf of load, while a 6-inch thick slab can support an estimated 18,000 to 20,000 psf. This represents an increase in load-bearing capacity of around 6,000 to 7,000 psf.
PSF stands for "pounds per square foot." It is a unit of measurement used to express the load or pressure exerted on a surface or structure. In the context of concrete driveways, psf represents the amount of weight the driveway can support per square foot of its surface area.
This measurement is important when determining the load-bearing capacity of a concrete driveway and ensuring it can adequately support the weight of vehicles and other equipment.
Choosing the Best Concrete Mix for Residential and Commercial Driveways
The best concrete mix for both a residential and a commercial driveway typically consists of a 4,000 psi mix with the appropriate type of Portland cement, coarse and fine aggregates, and water.
A minimum compressive strength of 3000 psi can be used for a residential single car driveway in a climate where no freeze thaw cycle occurs.
Admixtures can be added as needed to enhance performance and address specific project requirements. By choosing a high-quality concrete mix, you can ensure a durable, long-lasting, and high-performance driveway that meets the needs of both residential and commercial applications.
Expansion and Contraction Joints in Concrete Driveways
How concrete thickness relates to installing control joints.
Concrete expands and contracts as temperatures change, and the ground beneath the driveway can shift due to moisture content and other factors. Expansion and contraction joints serve several purposes:
- Accommodate Movement: Joints provide a controlled location for the concrete to expand and contract, helping to prevent uncontrolled cracking and damage.
- Stress Relief: Joints help to relieve stress within the concrete, redistributing it to prevent structural damage.
- Isolation: Joints can also be used to separate the driveway from adjacent structures, such as buildings, sidewalks, or other driveways, preventing damage due to differential movement.
Expansion and contraction joints are typically installed during the concrete pouring and finishing process. Here's a general overview of their installation:
- Layout: The joint pattern should be planned before pouring the concrete. Joints should be spaced at regular intervals and follow a specific pattern to ensure adequate stress relief and movement control.
- Installing joints: Contraction joints can be formed by cutting grooves into the surface of the freshly poured concrete using a jointing tool or by cutting the hardened concrete the next day using a concrete saw. The depth of the cut should be approximately one-quarter to one-third of the slab thickness.
- Isolation: Expansion joints are formed using pre-molded joint material, such as fiberboard or foam, which is placed between the concrete slabs or against adjacent structures. The joint material should be of the same thickness as the concrete thickness.
A general guideline for contraction joint spacing is to have joints at distances in feet equal to 2 to 3 times the slab thickness in inches. For example:
- 4-inch thick concrete: Joints should be spaced approximately 8 to 12 feet apart.
- 5-inch thick concrete: Joints should be spaced approximately 10 to 15 feet apart.
- 6-inch thick concrete: Joints should be spaced approximately 12 to 18 feet apart.
Thickening the Edges of a Concrete Driveway
It's a good idea to make the edges of a concrete driveway thicker than the middle, as it offers several benefits in terms of strength and durability.
This technique, called edge thickening or edge haunching, is used to reinforce the most vulnerable part of the driveway and provide additional support.
Benefits of Thicker Edges:
The edges of a concrete driveway are more prone to cracking and damage due to the following reasons:
- Vehicle Load Distribution: When vehicles drive near the edge of the driveway, the weight is concentrated on a smaller area, leading to increased pressure on the edges.
- Soil Support: The edges of the driveway often have less soil support than the middle, making them more susceptible to movement and settlement.
- Erosion: Water runoff and other external factors can cause soil erosion along the edges, weakening the support for the concrete slab.
By thickening the edges of the driveway, you can address these issues and provide the following benefits:
- Increased Strength: The additional concrete provides extra support and strength to resist the concentrated loads and stresses on the edges.
- Improved Durability: Thicker edges help to prevent cracking and damage due to soil movement, erosion, and other factors, ensuring a longer-lasting driveway.
- Enhanced Load-Bearing Capacity: Thicker edges can better support the weight of heavy vehicles, making the driveway suitable for a wider range of applications.
how to create thicker edges for a poured concrete driveway
To create thicker edges during the installation of a concrete driveway, follow these general steps:
- Excavation: When excavating the area for the driveway, dig a trench along the edges that is deeper than the middle section. The additional depth will typically range from 2 to 4 inches, depending on the desired thickness and load requirements.
- Subgrade Preparation: Compact the subgrade and install the gravel base as usual, ensuring that the edges are appropriately sloped for the thicker concrete.
- Formwork: Set up the formwork for the driveway, taking into account the increased thickness at the edges.
- Pouring and Finishing: Pour the concrete and finish it as usual, making sure to maintain the desired edge thickness throughout the process.
in conclusion:
In conclusion, the ideal concrete driveway thickness depends on various factors such as soil conditions, climate, expected traffic loads, and local building codes.
For residential driveways, a 4-inch thickness is typically sufficient, while commercial driveways often require a minimum of 6 inches. By considering these factors and consulting with an experienced concrete contractor, you can ensure your concrete driveway will be built to last.
Learn how to pour a diy concrete driveway.
Also, find out how much a concrete driveway costs.














