what are the correct CONCRETE MIXING RATIOS
Updated March 16, 2025
Author: Mike Day
When making your own concrete it's important to use the correct concrete mixing ratios to produce a strong, durable concrete mixture.
Some basic mixing ratios for concrete are 1:2:3, 1:3:3, 1:2:4. These mixing ratios are based on the proportions of cement : sand : stone in that order. The ratio you use will depend on what psi strength you need.
a good mixture for concrete has 4 basic ingredients
To make concrete there are four basic materials you need:
- Portland cement - You can buy this in a 94lb bag
- Sand - Course or Fine will work (course sand will give you a stronger mix)
- Aggregate (stone) You can use 3/8", 1/2", or 1/5" stone for aggregate
- Water - Clean cool water is best.
 I'm mixing 1 shovel of cement, 3 shovels of sand, and 3 shovels of stone with water to mix this concrete.
I'm mixing 1 shovel of cement, 3 shovels of sand, and 3 shovels of stone with water to mix this concrete.Here’s a breakdown of how different concrete mix ratios
apply to specific construction scenarios:
1:2:3 (High-Strength Mix - 4000+ PSI)
Best For:
- Structural concrete (columns, beams, foundations)
- Heavy-duty pavements
- Reinforced slabs
Why?
- High cement content increases strength and durability.
- Suitable for load-bearing structures where compression strength is crucial.
- Works well in freeze-thaw environments with proper curing.
1:2.5:3 (General-Purpose Mix - 3500 PSI)
Best For:
- House foundations
- Garage floors
- Sidewalks
Why?
- Good balance of strength and workability.
- More cost-effective than high-strength mixes while still durable.
- Suitable for moderate load-bearing applications.
1:3:3 (Standard Mix - 3000 PSI)
Best For:
- Driveways
- Patios
- Residential walkways
Why?
- Provides sufficient strength for foot traffic and light vehicle loads.
- Easier to work with and finish than higher-strength mixes.
- Commonly used for exterior slabs in residential settings.
1:3:4 (Low-Strength Mix - 2500-3000 PSI)
Best For:
- Non-load-bearing walls
- Decorative concrete elements (planters, benches)
- Indoor flooring where high strength isn’t required
Why?
- Increased aggregate content makes it more economical.
- Suitable for projects where appearance is more important than strength.
- Works well for artistic or lightweight concrete applications.
1:4:6 (Lean Mix - 2000-2500 PSI)
Best For:
- Footings and leveling concrete
- Base layers under structural slabs
- Temporary construction elements
Why?
- Low cement content reduces cost.
- Provides enough strength for non-structural applications.
- Used as a filler layer before pouring higher-strength concrete.
specialty mixes
Stamped Concrete (1:2:3 + Color Additives & Plasticizers)
- Used for decorative patios, driveways, and pool decks.
- Requires controlled curing and sealers to maintain aesthetics.
Self-Leveling Concrete (High Cement-to-Sand Ratio + Additives)
- Used for indoor flooring under tile or hardwood.
- Provides a smooth and even surface with minimal effort.
Fiber-Reinforced Concrete (1:2:3 + Fibers)
- Used in industrial floors, parking lots, and earthquake-resistant structures.
- Reduces cracking and improves durability.
concrete mixing ratio chart
A good concrete mixture is a specific blend of cement, water, aggregates, and admixtures used to create concrete.
The ratio of each ingredient used in the mixture determines the strength, durability, and workability of the resulting concrete.
Different types of concrete mixtures are used for different purposes, such as for foundations, walls, and slabs.
Below are some different mixing ratios based on the strength of concrete you need:
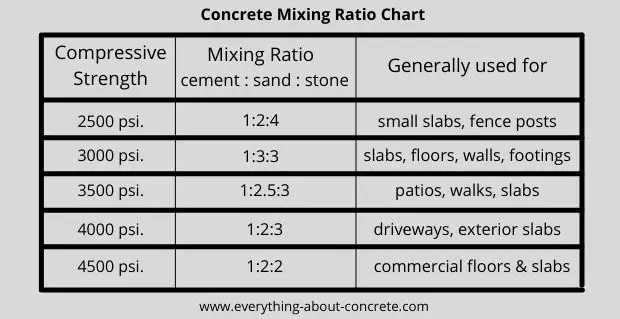
Listed above are some standard concrete mixing ratios used in the U.S.
mpa concrete mixes:
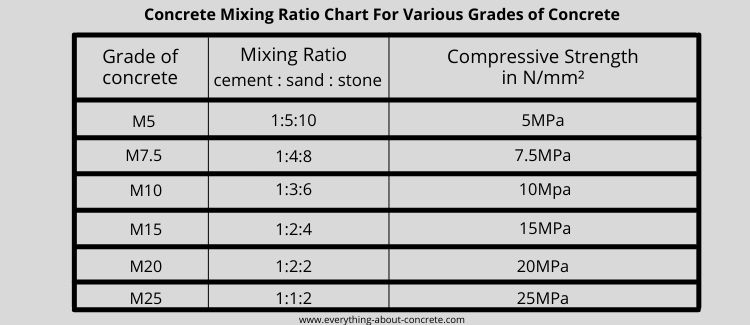
Listed above are some standard concrete mixing ratios for the rest of the world.
The Importance of the Water-to-Cement (W/C) Ratio in Concrete Strength and Durability
The water-to-cement ratio (W/C ratio) is one of the most critical factors in determining the strength, durability, and workability of concrete.
It represents the weight of water compared to the weight of cement in the mix.
How the W/C Ratio Affects Concrete
1. STRENGTH
- A lower W/C ratio (e.g., 0.40) results in stronger, denser concrete with higher compressive strength.
- A higher W/C ratio (e.g., 0.60) weakens concrete, increasing porosity and reducing strength.
2. DURABILITY
- Durability Lower W/C ratios improve resistance to freeze-thaw cycles, chemical exposure, and abrasion.
- Higher W/C ratios make concrete more prone to shrinkage, cracking, and water penetration.
3. WORKABILITY
- Higher W/C ratios make the mix easier to pour and finish, but too much water leads to segregation and bleeding.
- Lower W/C ratios require plasticizers or superplasticizers to maintain workability without compromising strength.
Safety Measures During Concrete Mixing and Handling
Concrete mixing and handling can be hazardous if proper precautions aren’t taken.
DIY enthusiasts and professionals should follow these safety measures to prevent injuries and ensure a safe working environment.
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Wearing the right protective gear minimizes exposure to harmful substances and reduces injury risks.
✅ Gloves – Use alkali-resistant rubber gloves to protect hands from cement burns.
✅ Safety Glasses/Goggles – Shields eyes from dust, splashes, and debris.
✅ Respirator/Mask – Wear an N95 mask when working with dry cement to avoid inhaling silica dust.
✅ Long-Sleeved Clothing & Pants – Prevents skin contact with wet concrete, which can cause chemical burns.
✅ Steel-Toe Boots – Protects feet from heavy objects, such as bags of cement or tools.
🚫 Avoid wearing shorts, open-toed shoes, or synthetic fabrics that can absorb chemicals.
2. Safe Mixing Practices
When mixing concrete, be mindful of potential hazards related to materials, equipment, and physical strain.
🔹 Add Water Gradually – Pour water slowly to avoid splashing and improper mixing.
🔹 Mix in a Ventilated Area – Cement dust can cause lung irritation; mix outdoors or in well-ventilated spaces.
🔹 Use a Sturdy Mixing Container – Whether using a wheelbarrow, bucket, or concrete mixer, ensure it’s stable and won’t tip over.
🔹 Follow Manufacturer’s Instructions – Different cement brands or additives may have specific handling guidelines.
3. Handling and Transporting Concrete Safely
Improper handling can lead to strains, spills, and injuries.
✅ Lift With Your Legs, Not Your Back – Cement bags are heavy; always use proper lifting techniques or a cart.
✅ Use a Helper When Pouring Large Batches – Wet concrete is heavy; teamwork prevents strain injuries.
✅ Be Cautious Around Moving Parts – When using a mechanical mixer, keep hands and tools away from rotating parts.
✅ Clean Spills Immediately – Wet concrete hardens quickly, so clean work areas promptly.
4. Preventing Skin & Eye Contact
Cement is highly alkaline and can cause chemical burns if left on the skin for too long.
⚠️ If concrete splashes into your eyes → Rinse with clean water for 15 minutes and seek medical attention immediately.
⚠️ If concrete contacts your skin → Wash with soap and water; do NOT use vinegar or lemon juice (they can worsen burns).
⚠️ Remove contaminated clothing → Wet cement can soak through fabric and cause burns without immediate signs.
5. Safe Cleanup and Disposal
After finishing the job, proper cleanup ensures safety and extends the life of your tools.
🛠️ Clean tools immediately – Dried concrete is difficult to remove.
🗑️ Dispose of excess concrete properly – Do not pour down drains; let it harden and dispose of it in a designated area.
💧 Wash hands thoroughly – Use pH-neutral soap instead of harsh detergents.
By following these safety measures, DIYers and professionals can reduce health risks and work efficiently when handling concrete.
What's a good concrete mixing ratio for a slab?

One of the best mixture ratios for a concrete slab is 1 : 3 : 3 (cement : sand : stone), this will produce approximately a 3000 psi concrete mix.
This mixing ratio is excellent for a shed slab, but it's also good for most concrete patios, footings, steps, and foundation walls.
The proper mixture of water with the cement, sand, and stone forms a paste that coats the stone and binds the materials together after the mix hardens.
The strength of the concrete will depend on how much water you use to mix it all together.
Basically this means the more water you use to mix the concrete (very fluid) the weaker the concrete mix.
The less water you use to mix the concrete (somewhat dry but workable) the stronger the concrete mix.
Accurate concrete mixing ratios can be achieved by measuring the dry materials using buckets or even a shovel.
Which Concrete to use: When I order ready mix concrete for a slab like the one above, I ask the concrete dispatcher for "a 3000 psi mix with 3/4 stone, micro-fiber, air-entrainment, and water reducer.
3000 psi concrete mix ratio for 1 cubic yard
1 : 3 : 3 MIX RATIO
To produce a 3000 psi cubic yard of concrete (27 cubic feet) the concrete mixture ratio is:
- 517 pounds of cement or (234kg)
- 1560 pounds of sand or (707kg)
- 1600 pounds of stone or (725kg)
- 32 - 34 gallons of water or (132L)
This mixing ratio will give you a concrete mix that is strong, durable, and good for most concrete projects.
A cubic yard of concrete will fill an area 8 feet wide by 10 feet long by 4 inches thick, or 80 square feet @ 4 inches thick.
At 6 inches thick a cubic yard of concrete will fill an area 52 square feet and at 5 inches thick, it will fill an area that's 65 square feet.
4000 psi concrete mixing ratio for 1 cubic yard
1 : 2 : 3 MIX RATIO (approx.)
To produce a cubic yard of 4000 psi concrete, you have to adjust the concrete mixing ratio to:
- 611 pounds of cement or (277kg)
- 1450 pounds of sand or (657kg)
- 1600 pounds of stone or (725kg)
- 33- 35 gallons of water or (133L)
As you can see, a little more cement and a little less sand is required to produce a stronger concrete mix that's used for driveways, pool decks, sidewalks, exterior patios, and commercial garages.
Knowing the weight of the materials and how much water to use should help you determine how much cement, sand, and stone to purchase to complete your project.
For estimating purposes, you can make about 1 cubic yard of concrete with 5.5 94-pound bags of cement, 17 cubic feet of sand, and 18 cubic feet of gravel. (It takes about forty 80-pound bags of prepackaged materials (like Quikrete) to make 1 cubic yard of concrete.)
Or... 1 cubic meter of concrete will require approximately 7.15 bags of Portland cement, .48 cubic meters of sand, and .51 cubic meters of gravel.
These are some tools that make mixing concrete easier
- A mixing tub for mixing the ingredients in
- A wheel barrow for mixing in and transporting the concrete
- A mason hoe for blending / mixing the concrete
- A shovel with a fiberglass handle
- An electric mixer for faster mixing
- A 1/4 horsepower electric concrete mixer
- A water bucket
- Water proof gloves (cement paste can burn your skin)
- Safety googles
- Add color to the concrete mix
Learn how to make concrete without a mixer, just mix it by hand.
how do you calculate a smaller concrete mix ratio?
If you need less than 1 cubic yard of concrete (or if ready-mix is not available) you can mix your own concrete on site either by hand, using the tools above, or by using an electric concrete mixer like the one in the link above.
To make smaller batches of concrete, use the same
proportions, but with smaller quantities, substituting buckets for
cubic feet. (For the mix proportions given previously, you'd use 1
bucket of cement, 3 buckets of sand, 3 buckets of stone, and 1/2 bucket
of water.)
For any batch size, the most important thing is to keep the proportions of the ingredients the same.
You can double or triple the
batch size simply by doubling or tripling the number of buckets for each
ingredient you add to the mixture.
what is the 1:2:3 mix ratio for concrete?
The mix ratio of 1:2:3 consists of 1 Part cement, 2 Parts sand, and 3 Parts stone (plus some water) to make a concrete mix you can use for most any building project.
The way you measure the ratio could be in shovels, buckets, or wheel barrows. As long as you're consistent you'll get a good strong mix.
Generally, when the stone ratio is more than the sand, this concrete cures a little stronger than a 1:3:3 ratio. The difference is in the workability of the concrete. The sand tends to make the concrete a little more easier to work with. The less sand the rockier the mix is going to be.
Cool things you can make by mixing your own concrete
- Concrete molds for making walkways
- Concrete forms and molds for making a patio
- Make concrete look like old wooden boards for stepping stones
- A turtle stepping stone
- Concrete planter's
- Concrete edging for your lawn or garden
what is the standard mix ratio for BAGGED concrete?
A pre-packaged bag is basically a 1 : 2 : 4 mixture for concrete, this is the standard for a lot of concrete mixtures.
These concrete mixture ratios are designed for the concrete to reach full strength at or around 28 days old.
Curing the concrete can be done by keeping it wet after the first day until the concrete is 7 days old.
Curing is an important step to take for the concrete to achieve full strength by 28 days.
video about concrete mixing ratios
Watch my video talking about what concrete mixing ratios and what it takes to achieve 3000 psi, 3500 psi, 4000 psi, and 4500 psi concrete.
I also break down the equivalent 20mpa, 25mpa, 30mpa, and 35mpa concrete mixing ratios.
See the video HERE.
concrete mix ratio calculator
Below you can use this concrete mix ratio calculator to determine how many cubic yards and bags of concrete mix it will take to do your project.
Make sure to use the proper dimensions (Feet and Inches, or Meters and centimeters) to get accurate results.
Once you know how many cubic yards or meters (or how many bags) it's going to take, you can figure out the weight and proportions of cement, sand, stone from there.
EXAMPLE: A project that takes TEN 80 lb bags of concrete mix, means you need 800 lbs of material.
A 1:3:3 mixing ratio calculates to 115 lbs of cement to 343 lbs of sand and 343 lbs of stone. (Rounded off)
LEARN HOW TO INSTALL YOUR OWN CONCRETE SLAB!
If you've ever thought of installing your own concrete slab but didn't know how or was unsure of the proper steps to take, well now you don't have to worry.
My course: How to form and pour a concrete slab just like the pro's do.
Will teach you each and every step you need to take to successfully install any size concrete slab.
Check it out, this course could save you hundred's of dollars by teaching you how to install a concrete slab by yourself.
Click HERE to get it now.
frequently asked questions
Here are some answers to frequently asked questions about mixing concrete:
What is the ideal concrete mixture ratio for foundations?
- A common concrete mixture ratio for foundations is 1:2:3 (cement: sand: gravel) with a water-cement ratio of 0.5.
- What is the best concrete mix for a garage floor? The garage floor mix I use for all my garage floors is a 3500 psi. mix with 3/4 stone, micro-fiber, air-entrainment, and water reducer.
Can I change the mixture ratio depending on the application?
- Yes, the mixture ratio can be adjusted depending on the intended use of the concrete. A higher strength concrete will require a different mixture ratio than a lower strength concrete.
How do I determine the right mixture ratio for my project?
- The right mixture ratio depends on several factors, including the strength required, type of cement used, and the aggregates used. Use a concrete strength calculator and follow the recommended mix ratios.
Can I use more water to make the concrete easier to work with?
- Adding too much water to the mixture will weaken the concrete and make it more prone to cracking. Always follow the recommended water-cement ratio.
What happens if I use too much cement in the mixture?
- Using too much cement in the mixture can make the concrete brittle and prone to shrinkage. Always follow the recommended mix ratios.
Can I use different aggregates in the mixture?
- Yes, different types of aggregates can be used in the mixture. However, they must be compatible with the cement and have the right particle size.
Can I add more cement to the mixture to make it stronger?
- Yes, adding more cement to the mixture can make the concrete stronger, but make sure to follow the recommended mixing ratios or the concrete could be more susceptible to shrinkage cracks.
Can I mix the concrete by hand instead of using a mixer?
- Mixing concrete by hand is possible, but it can be difficult to achieve a consistent blend. It's recommended to use a concrete mixer for best results.
How long does it take for concrete to dry and cure?
- Concrete dries and cures at different rates depending on the temperature and humidity. It takes about 28 days for concrete to reach its full strength.
Can I use admixtures in the mixture?
- Yes, admixtures can be added to the mixture to enhance specific properties of the concrete, such as setting time, workability, or durability. Always follow the recommended dosages.
For more on concrete slabs see the information below:
WHAT IS THE CONCRETE MIX RATIO OF 3000, 3500, 4000 AND 4500 PSI CONCRETE?
POURING A CONCRETE SLAB
THANK YOU FOR SUPPORTING EVERYTHING-ABOUT-CONCRETE.COM
This page includes affiliate links. When you click on any link from everything-about-concrete to Amazon or other affiliate sites and purchase a product, E-A-C receives a commission on the sale. It doesn't cost you a penny and helps support the site THANK YOU!
Return from Concrete mixing ratios to Concrete slab
Return from Concrete mixing ratios to Everything About Concrete home page













